9. Six Levels of AI Integration: A Business Framework Inspired by Autonomous Vehicles
As business leaders continue to navigate the rapidly evolving landscape of artificial intelligence, we must make strategic decisions about where AI can be effectively applied and where human expertise remains essential. In our previous post, we explored the importance of balancing AI adoption with human ingenuity. Now, we'll leverage the well-known framework for Autonomous Driving to develop a framework for AI implementation in businesses, from no automation to transformation.
A Framework For Autonomous Driving
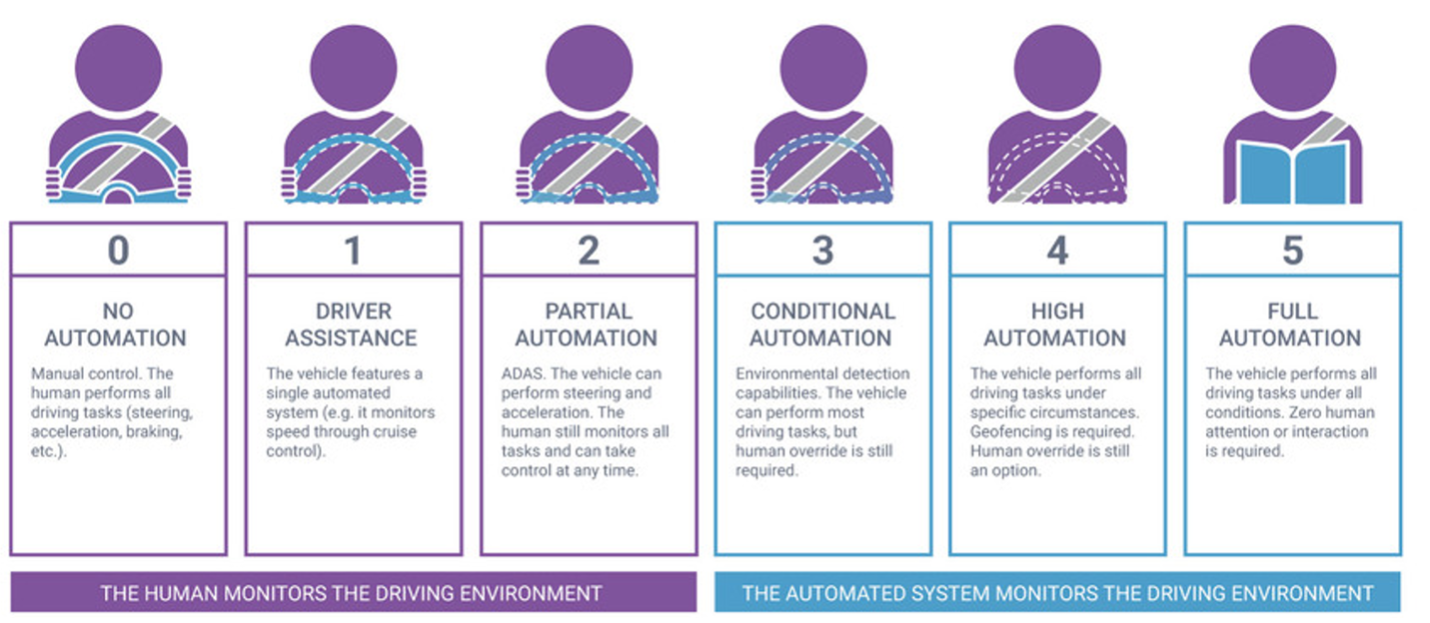
The Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) defines six levels of automation for autonomous vehicles, ranging from Level 0 (no automation) to Level 5 (full automation; illustration below).
I was inspired by the simplicity of the above framework, and below is my adaptation of it for AI implementation in businesses; enabling leaders to navigate the different stages of AI adoption and process automation.
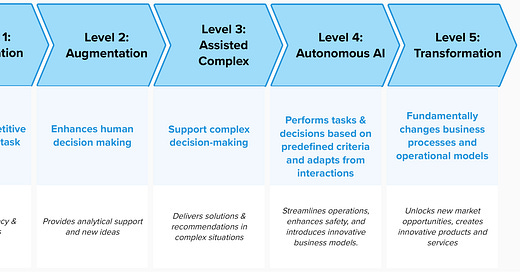
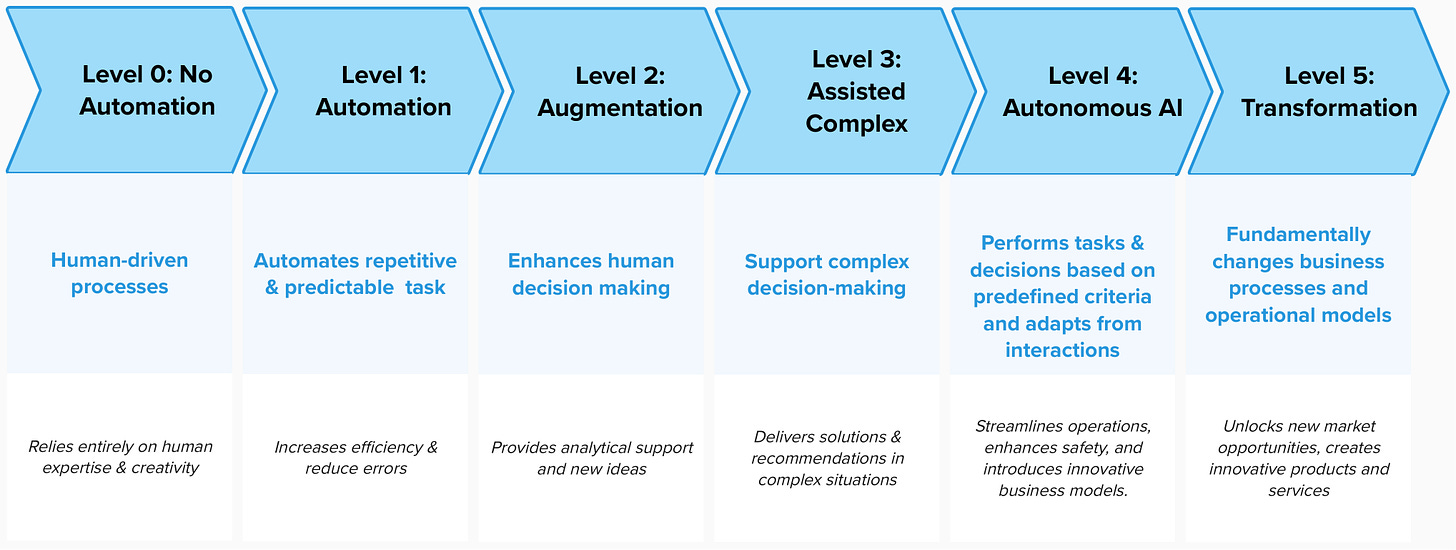
Six Levels of AI Implementation in Business Processes
Level 0: No Automation - Human-Driven Processes
Description: Entirely manual processes relying solely on human effort and decision-making.
Opportunities: Maximizes human expertise, creativity, and intuition
Challenges: Prone to human error, inefficiencies, and difficult to scale
Examples: Manual data entry, customer service, and decision-making
Level 1: Automation - AI-Assisted Processes
Description: AI automates repetitive and predictable tasks, supporting human work
Opportunities: Boosts efficiency, reduces manual errors and allows employees to focus on higher-value tasks
Challenges: Requires careful selection of “automatable” tasks, high standards for data quality, and integration with existing systems
Examples: Chatbots for handling standard inquiries, robotic process automation (RPA) for data entry, and machine learning-based automation for predictive maintenance
Level 2: Augmentation - AI-Enhanced Human Decision-Making
Description: AI provides insights, analytical support, and new ideas to augment human decision-making and creativity.
Opportunities: Enhanced decision-making, improved accuracy, and increased productivity
Challenges: Ensure data quality and “right” training data, existing IT infrastructure/capabilities, and the need to mitigate potential biases in AI models
Examples: Predictive analytics for sales forecasting, internally facing chatbots for employee productivity, AI-assisted legal research tools that expedite case analysis and preparation, content creation for ideation (video, text, and photo editing), and diagnostic aids in healthcare
Level 3: Assistance - AI-Assisted Complex Decision-Making
Description: AI assists with complex decision-making, offering solutions and recommendations that require a deeper understanding of operational contexts and human needs.
Opportunities: Improved customer experience, increased engagement, and enhanced strategic decision-making
Challenges: Critical to maintain data quality and “right” training data, ensure integration with core systems, and address ethical issues in AI applications
Examples: AI-driven customer service platforms that anticipate and solve consumer issues before they arise, content curation engines that tailor learning experiences for individual students, and clinical decision support systems that provide real-time data analysis to assist in complex medical diagnoses
Level 4: Autonomous - AI-Operated Processes
Description: AI operates independently without ongoing human oversight, capable of making decisions and performing tasks based on predefined criteria and learning from interactions. But mechanisms for human oversight are maintained.
Opportunities: Increased operational efficiency, improved safety, and new business models
Challenges: Ensuring safety, addressing ethical concerns, and integrating with existing systems
Examples: Self-piloting drones that manage agricultural monitoring, smart manufacturing systems that autonomously adjust production schedules and processes based on demand forecasts, and AI-managed energy grids that optimize distribution and consumption without human intervention
Level 5: Transformation - AI-Driven Business Innovation
Description: AI fundamentally changes business processes, operational models, or entire industries, creating new ways of working, innovative products, and services that transform the status quo. While AI introduces new ways of working and groundbreaking products, human oversight is still required to ensure alignment with ethical standards and organizational goals.
Opportunities: Identify new market opportunities, innovative products and services, and first-mover advantages
Challenges: Addressing ethical concerns, ensuring accountability, and integrating with existing systems
Examples: AI-powered drug discovery, AI-generated content for entertainment, and AI-driven business model innovation such as Everything On Demand, AI Learning & Career Development, and AI-Driven Privacy & Authenticity
Where is your organization focused?
It is crucial to understand what level your initiatives are focused on and how you can leverage AI for growth and efficiency. Here are some actionable steps to begin this transformation:
Identify areas where AI can augment or automate tasks
Assess data quality and availability
Develop a clear understanding of business goals and objectives
Start with small pilot projects and scale up
Continuously monitor and evaluate AI solutions
By understanding these levels and their applications, business leaders can better understand where they are on their journey and where is there still runway to unlock new growth or efficiency opportunities. In our next post, we'll explore a comprehensive framework for developing an AI strategy aligned with business goals.